
The Company
Topics
Contacts

nonwovens finishing lines
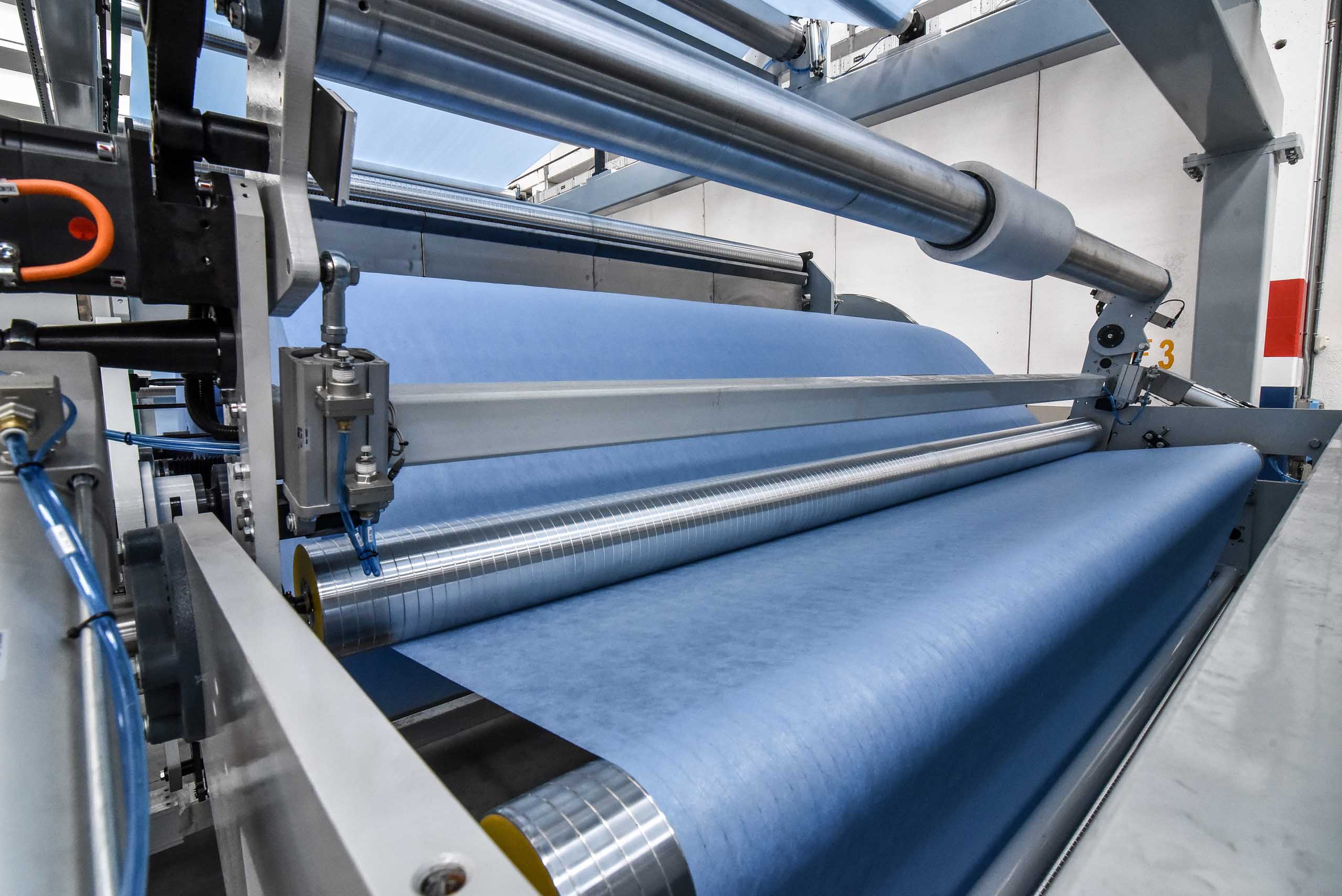

Lamination is the process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the combined physical and mechanical characteristics of each layer make for a stronger, more resilient composite material.
The earliest examples of lamination made use of natural adhesives such as beeswax, gums, tar and substances derived from animal bones. As technology progressed, we discovered the use of sealing wax as the first hot-melt adhesive.
In the 1930s a wet lamination process (with the use of solvents) was used to bond shirt collars (a woven fabric) with cellulose acetate. This process was deemed inconvenient, and by 1948 progress was made in dry lamination using polyvinyl acetate plasticized with dibutyl phthalate.
Nonwovens lamination, in particular, is the process of bonding two or more layers, at least one of which is a nonwoven fabric, with the aim of obtaining better strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance or other properties.
The bonding is typically done with the use of adhesives (or heat) and pressure, making it possible to manufacture nonwovens products, equipped with a waterproof layer, that are breathable, soft, comfortable and suitable for printing.
Shortly after the beginning of the industrial production of disposable diapers, nonwoven laminated products, such as the textile backsheet, appeared. From the early days of dry lamination various adhesives were produced, including hot-melt powders.
Breathability was an issue with lamination in the early days, but the processes used today are capable of producing breathable, porous materials that maintain their waterproof properties.
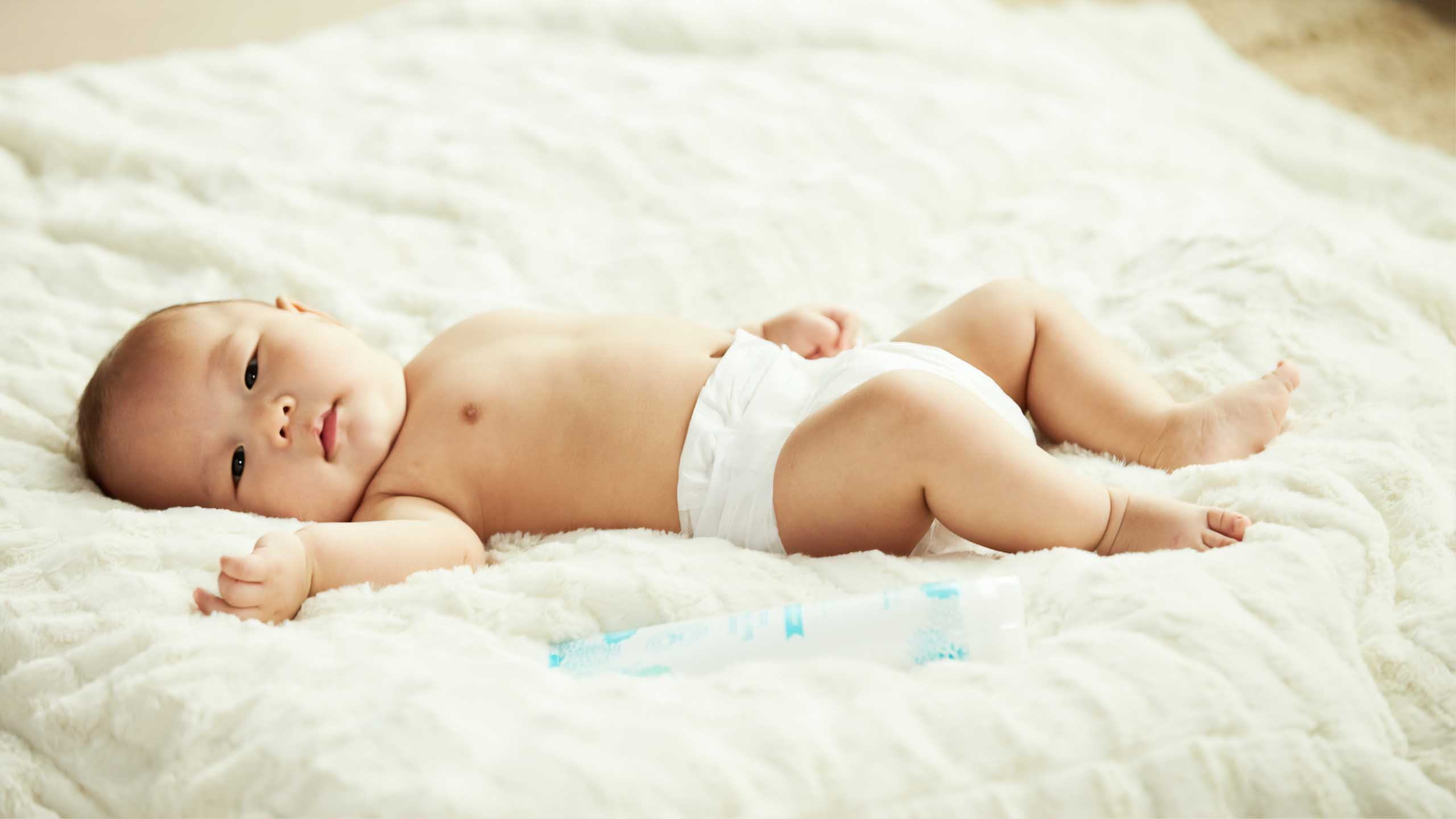

The use of nonwoven laminates has grown over the past few decades to include many industries, such as agriculture, clothing (interlinings, fillings, etc.), household, transportation and environment. While there are many uses across various industries, the following make the most use of nonwoven laminates.
The medical industry is one of the most prominent users of nonwoven laminates. With the need to have sterile, disposable materials, there are a number of key uses for this material in medicine.
Nonwovens lamination creates breathable materials that allow moisture to easily pass out of the garment, while preventing liquids from entering. The nonwoven composite material can also have an anti-microbial surface treatment to further enhances its protective properties. The outer layer of nonwoven fabric is soft to the touch, strong and durable.
Read more: How to produce the best disposable Nonwovens Medical Textiles
Nonwovens lamination produces a variety of protective clothing and equipment in the medical field, such as:
Remember that all surgical gowns, masks, and protective coverings must be lightweight and fit snuggly, while allowing freedom of movement.
Read more: A.Celli Nonwovens in support of the Chinese health emergency
Hygiene is another industry that widely uses nonwoven laminated products. Again, the focus is on sterile, disposable products featuring air and water vapor permeability and water resistance like:
Read more: 3 Main process challenges in Textile Backsheet Lamination (+ How to solve them)
Filtration is used in many industries, including beverage and automotive. The filtration of air and liquids requires filters made using nonwoven laminates with the capability of filtering various sizes of particles, depending on the type of filter and intended use.
A coffee filter, for example, only has to filter out the coffee grounds and allow the water to pass through. In contrast, an air filter must be capable of filtering out the tiniest particles of dust and other contaminants to ensure purification. Here are examples of filters made using nonwoven lamination:
Read more: 6 Types of processes used to make Nonwoven Filter Media
The construction industry relies on materials made with nonwoven lamination primarily for insulation and waterproofing. The types of products used by the construction industry includes things like:
The most suitable lamination method depends on the required properties of the final composite which, depending on the specific application, might need to be:
As for the techniques that can be used in nonwoven lamination, these can be divided into four categories:
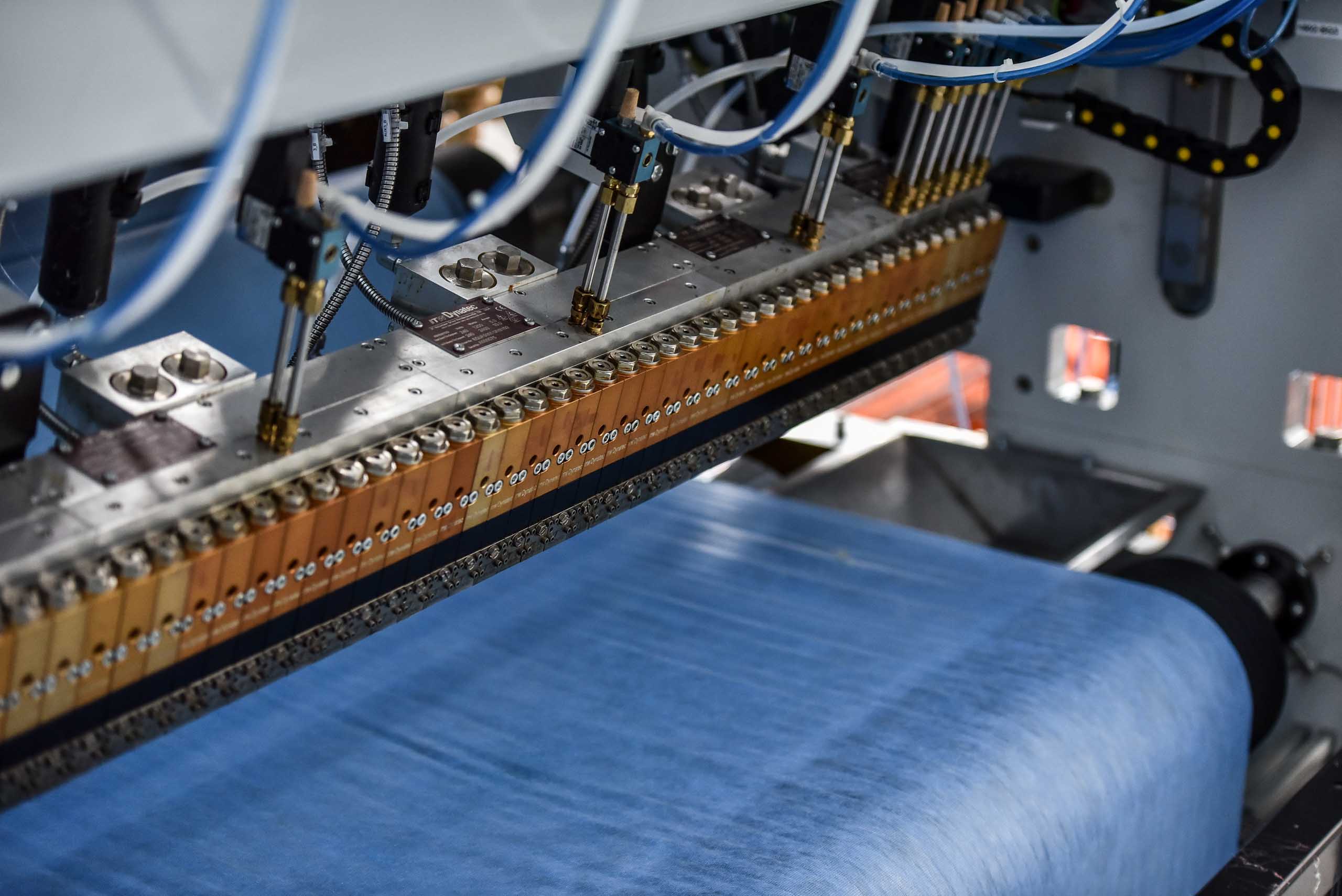
When it comes to adhesive nonwovens lamination, there are a number of different methods:
Using hot melt adhesives is the leading method, replacing older ones like mechanical fastening, cold glue and wet lamination. This method uses microscopic dots to create bonds between the layers in order to form a composite. It offers several advantages, including the ability to:
Thermal lamination uses pressure and heat to adhere layers together, using a thermoplastic layer that can be a hot melt, fiber, film, or powder. There are a few different thermal bonding options that can be used, including the following:
Read more: Adhesive and Thermal Lamination technologies explained for the roofing and construction sectors
Ultrasonic lamination is the most environmentally friendly method, since no chemicals or adhesives are required. It relies on the use of high-frequency sound vibration to generate heat locally, which in turn causes thermoplastic fibers to melt and bond. Aside from the sustainability of the process, the advantages of ultrasonic lamination are many, including the ability to:
Extrusion coating is a process in which a molten polymer is applied as a thin coating on one or both sides of one or more nonwoven layers.
This coating makes the nonwoven material waterproof, printable, antistatic and flame-resistant. In addition to this, the Extrusion Coating allows to contain the costs of raw materials and improve the structural stability of the material.
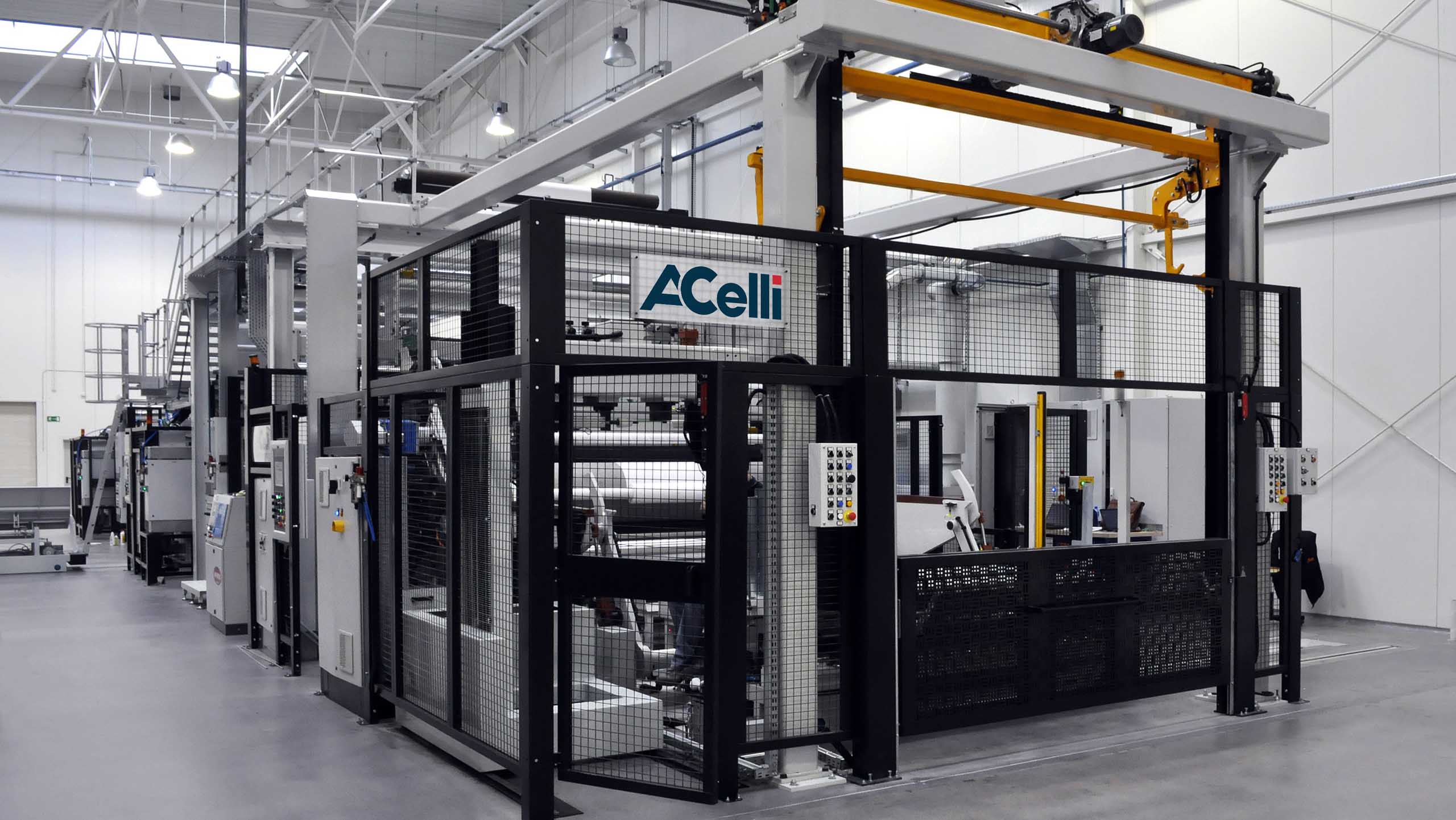

The characteristics that a good machine for nonwovens lamination must have are undoubtedly energy-efficiency, high production speed and great precision.
However, what truly sets the best machine apart is the dedicated quality and tension controls, two critical elements when it comes to the lamination of fragile material to ensure the high quality of the final product.
It is also important to remember that the nonwovens lamination machine is part of a larger system that includes machines dedicated to other tasks, and that it must work in sync with these other machines to ensure that the entire process from the beginning to the end of the system flows smoothly.
This means that when the nonwoven materials are laminated, the final composite must transition to the next machine, whether that is packaging, material handling or converting lines, without losing the properties or characteristics of the original materials.
In addition, the machine should provide:
The A.Celli F-LINE® complete turnkey line provides high-quality adhesive, thermal, and ultrasonic lamination, as well as unwind stands, laminating stations, and in-line slitting winders. This state-of-the-art machine is capable of laminating two or more layers with a maximum web width of 3,600 mm at a speed of 400/800 m/min. Moreover, among the optional components you can request you can find:
Contact us for more information about our A.Celli F-LINE® Lamination Solution or to request a free consultation.